Dpdl (Dynamic Packet Definition Language)
Dpdl is a rapid development programming language and constrained device framework with built-in database and agent technology.
The Dpdl language constructs and syntax is simple and intuitive, yet powerful, with an object oriented paradigm (OOP), interoperable with java JVM platform APIs and external Native shared libraries.
Dpdl comes as a very compact and portable execution engine (DpdlEngine) with an extensible API interface that enables to execute Dpdl code, as well as code in other programming languages or any custom syntax directly embedded within the same Dpdl source code, simultaneously and of multiple types.
The DpdlEngine provides access to java platform API’s, Native shared libraries, Wasm modules and GPU compute and enables the embedding and execution of multiple programming languages like C, C++, Python & MicroPython, Julia, JavaScript, Lua, Ruby, Java, PHP, Perl, Groovy,V, Clojure, Modelica, Wgsl and OpenCL, directly embedded within Dpdl code. Everything comes already included with the DpdlEngine, No additional installations required.
The core Dpdl engine has the capability to run also on memory constrained devices and platforms via a dedicated kilobyte range virtual machine.
Dpdl is Self contained, Compact, Portable and Customizable

Dpdl = Dpdl lang + ( C + Java + ‘C++’ + Python + Julia + JavaScript + Java + Lua + Ruby + PHP + Perl + Groovy + V + Clojure + Wat/Wasm + Wgsl + OpenCL + Modelica) + AI = Powerful and Versatile
Dpdl itself is a multi-purpose programming language, self-contained, interpreted and in part dynamically bytecode compiled, statically as well as dynamically typed, with a very compact memory footprint and portable to most platforms. There is an on-going development to enable Dpdl code to be compiled also directly to native code for multiple target platforms.
In addition Dpdl introduces the concept of ‘embedded code sections’ that can be executed within Dpdl code. It allows to create and integrate custom syntax and language interpreters of all sorts in form of ‘Dpdl language plug-ins’, for example code in other programming languages or any other custom code syntax.
Multiple ‘Dpdl language plug-ins’ are currently available, for example also for the ‘Modelica’ language for cyber-physical simulations is available as ‘Dpdl language plug-in’. Further Dpdl language plug-ins are currently in active development, for example to enable also Quantum Computing directly inside Dpdl.
The included Dpdl language plug-in ‘DpdlAINerd’ (DAN) enables to automatically generate via AI generative code programming language code and content or data by means of natural language descriptions contained inside Dpdl code, embed it automatically within Dpdl code and execute the code right away or alternatively to be written to a new file and executed in subsequent steps.
Further, the custom ‘DpdlPacket’ data container with built-in database technology provides a convenient way to package, handle and query data efficiently on memory scarce devices.
Dpdl is designed to:
- Develop ideas faster
- On multiple platforms
- Using the power of multiple programming languages and API’s within a single source
- Reuse code
- No need to install, compile and configure dev environments
- Self-contained, No additional dependencies required (except user libraries)
- Facilitate rapid prototyping for Hardware programming
- Runs on constrained devices
- Customizable
- Plug-in oriented
- Leverage prototyping with AI generative code
DpdlEngine stack overview
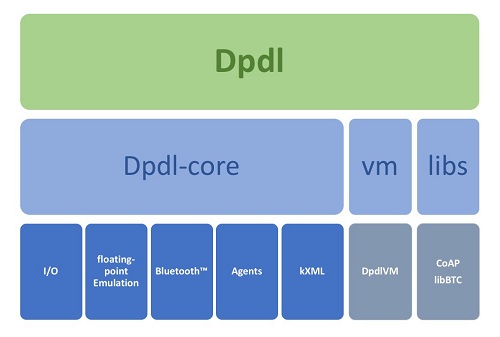
Compact, Robust, Extensible and Portable
Common IoT protocol stacks such as Bluetooth™ and CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) are integrated by default and third party libraries and protocols can be added as extensions.
Dpdl provides a simple access to java API’s, Native shared libraries, Wasm modules and GPU compute.
The included Dpdl language plug-in ‘DpdlAINerd’ (DAN) enables to make use of AI generative code to automatically generate and embed executable code and content or data by means of natural language descriptions contained inside Dpdl code.
The custom ‘DpdlPacket’ data container with built-in database technology provides a convenient way to package, handle and query data efficiently on memory scarce devices.
Dpdl enables the integration of different technologies to leverage fast prototyping and foster research and development.
Dpdl can be used as:
-
Rapid application development platform
-
Embedded scripting engine
-
Development of Domain Specific Languages (DSL)
-
Data handling on memory constrained devices
-
AI generative code
-
Library module
-
Testing framework for heterogeneous code bases
-
Utility tool
Features
-
DpdlEngine is optimized to run on a wide range of platforms (J2SE, any JVM platform > 1.3 Spec). The core engine runs also on Java 1.1 spec compliant VMs. This makes it possible to run Dpdl also on very small footprint Virtual Machines
-
Dpdl API provides access to the complete underlying Java JVM platform API’s and to external java
-
Access to Native shared libraries
-
Features meta-programming techniques: compile-time (CTMP) and runtime (RTMP) meta-programming
-
Automatic code generation and execution of embedded code sections at runtime
-
Multiple ‘Dpdl language plug-ins’ available (embeddable programming languages): C, C++, Python, MicroPython, Julia, JavaScript, Lua , Ruby, Java, PHP, Perl, Groovy, Clojure, Modelica, Wgsl and OpenCL programming language code can be embedded and executed directly within Dpdl code (interpreted/compiled code)
-
Everything is already included, No additional installations needed (except user libraries)
-
Further programming languages and syntax interpreters can be embedded via a dedicated kernel execution interface in form of plug-ins
-
Includes embedded C compiler: On-the-fly compilation of embedded ANSI C code in memory at runtime -> very Fast compile time!!!
-
Wasm runtime Dpdl language plug-in included allows to access ‘Wasm’ module functions from Dpdl and from embedded language code. Also WAT code can be directly compiled on-the-fly and executed
-
Built-in Dpdl scripting engine with support for custom extensions -> allows to dynamically add language features at runtime
-
Dpdl C-API enables to execute Dpdl code embedded within programs written in C
-
On the fly conversion/compilation of Dpdl types ‘class’ and ‘struct’ into native java bytecode classes
-
Support for common IoT protocol stacks such as Bluetooth™ (JSR-82) and CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) (IETF standard RFC 7252)
-
Distributed Agents (FIPA compliant)
-
Packing data in a ‘DpdlPacket’ is a convenient way to optimize and speedup access to data. The speedup is x 25 times faster compared to a standard record store access
-
Virtual record store filesystem
-
Double precision floating point emulation
-
XML with XPath
-
JSON
-
Easy integration of custom libraries
-
Small footprint, Only
372 Kbfor DpdlEngine -> can be stripped down to80 Kbfor minimal setup -
Allows to automatically generate and embed generative AI programming code within Dpdl using the ‘DpdlAINerd’ (DAN) Dpdl language plug-in
-
Allows to scale computations on GPUs using the ‘OpenCL’ and ‘Wgsl’ (WebGPU shading language) Dpdl language plug-in
-
Open Source programming language plug-ins
For more Info visit the official Dpdl-io repository on GitHub:
DpdlEngine
Prototype sample applications implemented with Dpdl can be found on this GitHub repository:
Dpdl-sample-Apps
Dpdl JVM/JRE access
Dpdl provides API functions to load and access java objects and methods of the underlying JVM platform and of any other external java libraries. This allows to use a broad set of API’s within Dpdl.
Dpdl Example using external Java libraries
This is a sample Dpdl app implementing a 3D model visualization of chemical molecules using the JavaFX library. The model can be rotated freely with mouse events.
graphics/dpdl3DJavaFX_molecule.h
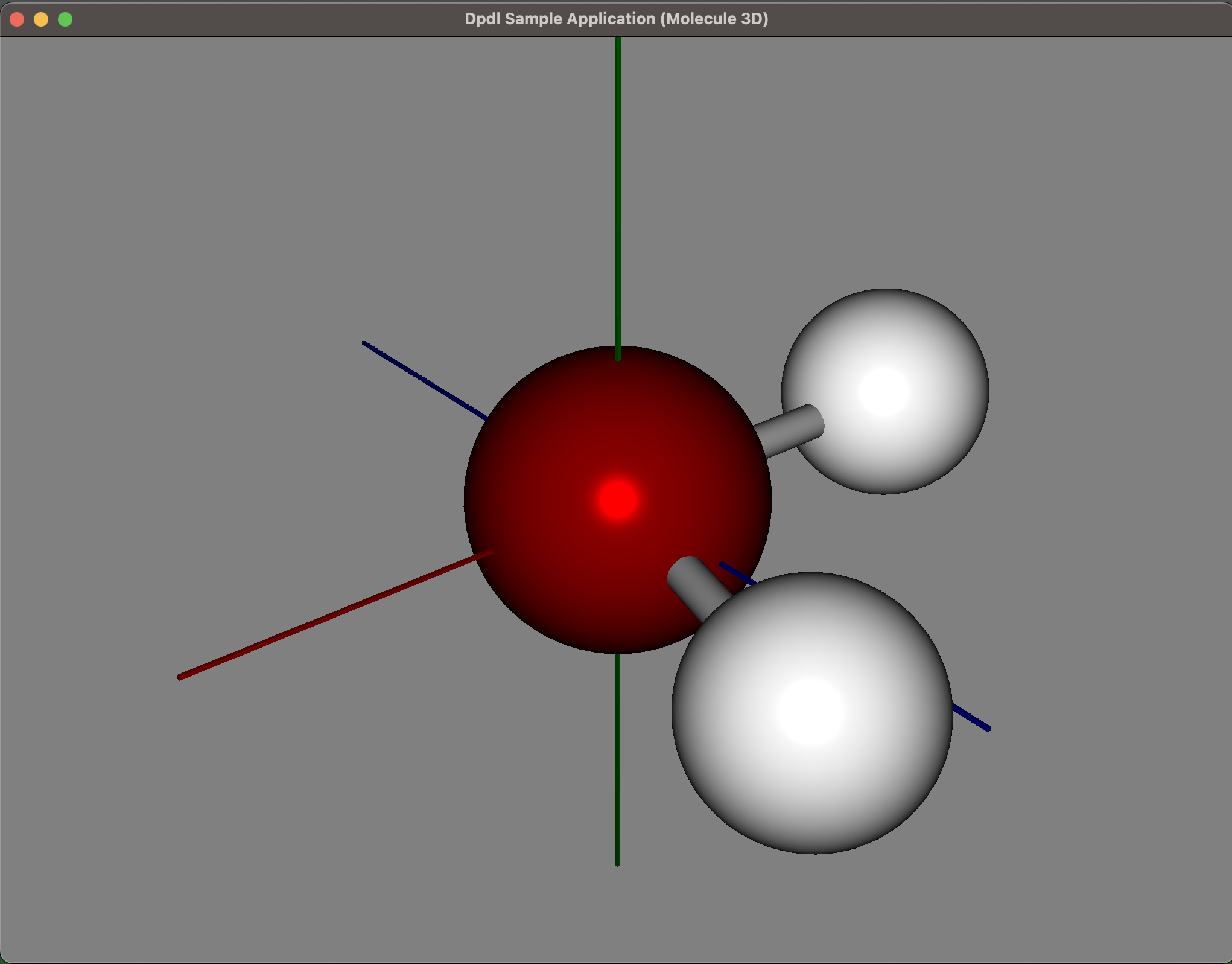
VIDEO of Dpdl sample 3D application
Dpdl language plug-ins ( ‘embedded code sections’ )
Multiple programming languages can be embedded and executed within the same Dpdl code via the keyword >>.
Further programming languages and syntax interpreters can be developed and integrated via a dedicated plug-in interface and configuration if form of Dpdl language plug-ins.
This enables basically every sort of programming language or natural language syntax interpreter to be embedded and executed directly within Dpdl code.
This features is very useful for rapid development and rapid prototyping and is also a key feature for generative code.
Currently the following programming languages can be embedded within Dpdl:
-
Ccode (interpreted) --> minimal subset of C90 with standard C libs included and available in the dpdl runtime -
Ccode (compiled ) --> ANSI C & ISO C99 standard, compiled in memory and dynamically executed at runtime -
C++ -
Python -
MicroPython(ideal for embedded systems) -
Julia -
JavaScript -
Lua -
Ruby -
OCaml -
Java -
PHP -
Perl -
Groovy -
Clojure -
Modelica
available add-on ‘Dpdl language plug-ins’:
-
Wasm-> WAT Compiler and Wasm Runtime -
Sql-> query databases via SQL -
Wgsl-> WebGPU shading language (WGSL) -
OCL-> Open Computing Language (OpenCL) -
AI-> see doc/DpdlAINerd.md
In development ‘Dpdl language plug-ins’ (available soon in coming releases):
quantum-> OpenQWASM compiler and executor to leverage Quantum Computing capabilities
Dpdl Example with ‘embedded code sections’
Sample Dpdl code with embedded ‘C’ code and ‘javascript’:
struct A {
string id = "A"
int x = 10
float f = 0.3
double d = 0.4d
object stro = new("String", "This is a java.lang.String object")
func print()
println("------------------")
println("id: " + id)
end
}
# main
println("With Dpdl you can make use of any java library and embed different programming languages...")
struct A mya
mya.print()
println("creating a hashmap to store key/value pairs...")
object mymap = new("HashMap")
mymap.put(1, "Dpdl")
mymap.put(2, "is")
mymap.put(3, "Simple")
mymap.put(4, "Compact")
mymap.put(5, "Portable")
object keys = mymap.keySet()
object iter = keys.iterator()
object key, value
for(iter.hasNext())
key = iter.next()
value = mymap.get(key)
println("key: " + key + " value: " + value)
endfor
bool bcon = mymap.containsValue("Dpdl")
println("mymap contains 'Dpdl': " + bcon)
println("")
println("Embed different programming languages directly..")
println("")
int n = 6
double x = 10.0d
string a = "test"
println("embedding C...")
dpdl_stack_push("dpdlbuf_var1",n, x, a)
>>c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <dpdl.h>
int dpdl_main(int argc, char **argv){
printf("Hello C from Dpdl!\n");
printf("\n");
printf("num params: %d\n", argc);
int cnt;
for (cnt = 0; cnt < argc; cnt++){
printf(" param %d: %s\n", cnt, argv[cnt]);
}
char *buf = "My result";
dpdl_stack_buf_put(buf);
return 0;
}
<<
int exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
println("embedded C exit code: " + exit_code);
string buf = dpdl_stack_buf_get("dpdlbuf_var1")
println("response buffer: " + buf)
println("")
println("embedding javascript...")
int val = 23
arr[] = [1, 2, 3, 4]
dpdl_stack_push(val, arr)
>>js
console.log('Dpdl sends a message with js');
var sa;
var arr;
var v;
if(scriptArgs.length > 1){
v = scriptArgs[0];
sa = scriptArgs[1];
arr = sa.split(",");
std.printf("val=%d\n", v);
console.log(arr);
}else{
sa = "";
}
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
std.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i, arr[i]);
}
<<
int js_exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
println("embedded javascript exit code: " + js_exit_code);
Supported Platforms
Dpdl runs on a wide range of platforms and includes also a small footprint kilobyte range java virtual machine that can be compiled for almost every platform as soon as an ANSI C compiler is available for the target platform.
‘DpdlEngine’ is compatible with:
-
Java versions > 1.3 and later
-
Java ME CLDC & GCF (JSR 360)
-
Java ME Embedded Profile (JSR 361)
-
Java 1.1 until 1.3 (without ‘new’ and ‘getObj’ functions)
-
All Platforms where the Open Source virtual machines like ‘JamVM’ and ‘miniJVM’ can be compiled
-
Platforms with ANSI C compiler where the included kilobyte range java virtual machine can be compiled
So far DpdlEngine V1.0 has been tested on:
- MacOS (aarch64)
- Linux (x86_64)
- Raspberry PI (armv7l)
- Windows 64-bit
- Android
- JavaME
- J2ME (MIDP 2.0)
Roadmap
Dpdl is currently developed by SEE Solutions and the following integrations are in development:
-
Back-end compiler to compile Dpdl code to native machine code for most target architectures
-
Dpdl-IDE with plug-ins for popular IDEs (IntelliJ, eclipse, VS Code)
-
Development of a dedicated ‘Dpdl language plug-in’ for enabling Quantum Computing via embedded OpenQASM 2.0 (Circuit description language) code within Dpdl
Docs
The Dpdl framework and API documentation are available via the following links:
Dpdl embedded minimal C library Documentation
More…
Visit also the official Dpdl-io repository on GitHub for updates: DpdlEngine
Dpdl Examples
Dpdl-sample-Apps
Full featured prototype applications developed with Dpdl are published on this GitHub repository:
Dpdl example with embedded ‘C++’ code that make use of the ROOT framework libraries
C++ code can be embedded within Dpdl with the keyord ‘>>cpp’
The following dpdl example makes use of an embedded code section in C++ that uses libraries from the the powerful ROOT Data Analysis Framework developed by CERN (https://root.cern/) .
Example Dpdl code embedding C++ with libs ‘ROOT’:
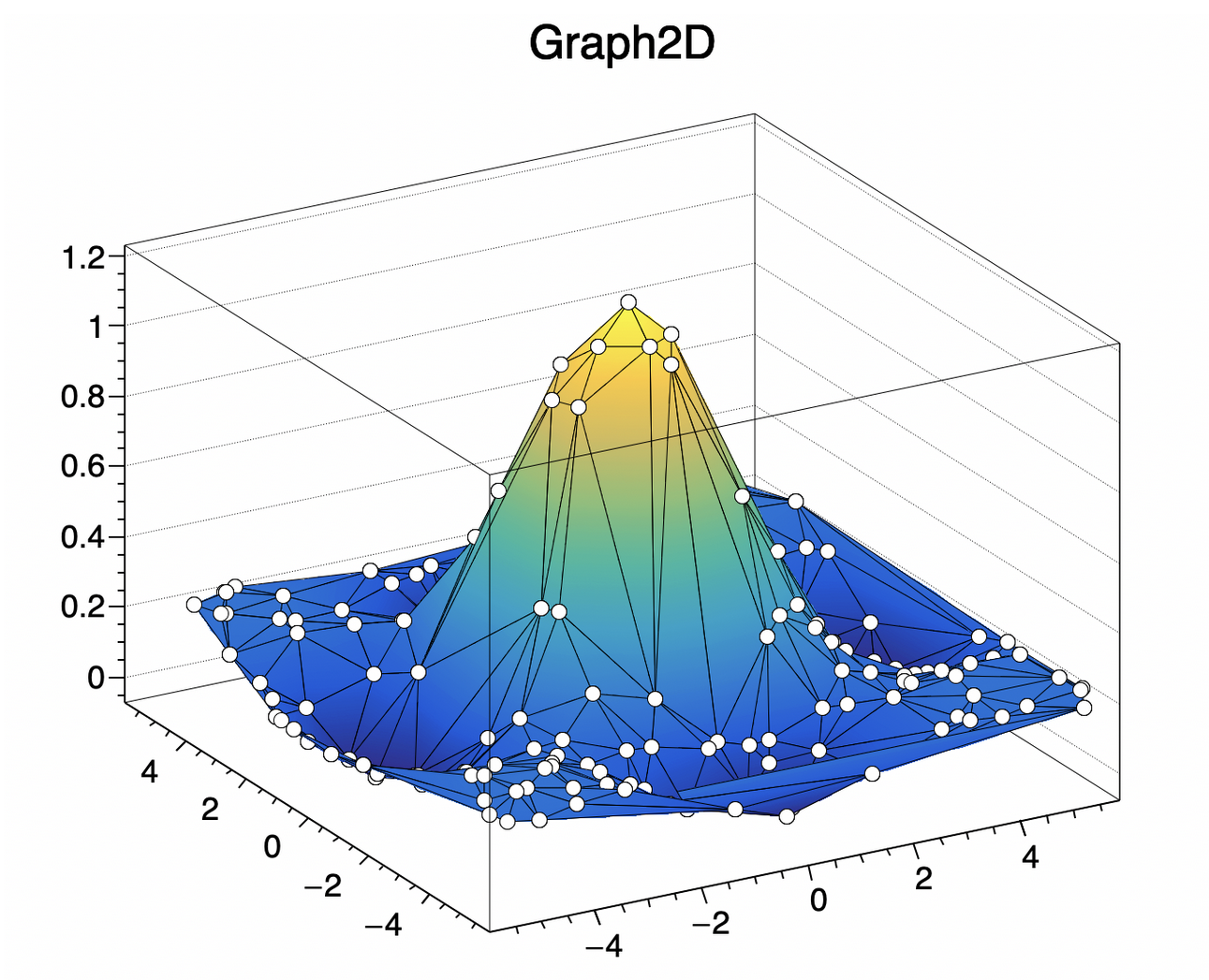
# main
println("test embedded ROOT C++...")
>>root
auto canvas = new TCanvas("c","Graph2D example",0,0,700,600);
double x, y, z, P = 6.;
int np = 200;
auto dt = new TGraph2D();
auto r = new TRandom();
for (int N=0; N<np; N++) {
x = 2*P*(r->Rndm(N))-P;
y = 2*P*(r->Rndm(N))-P;
z = (sin(x)/x)*(sin(y)/y)+0.2;
dt->SetPoint(N,x,y,z);
}
dt->Draw("tri1 p0");
canvas->Modified(); canvas->Update();
<<
int exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
println("embedded ROOT exit code: " + exit_code)
Sample Dpdl code that make use of type ‘class’ Inheritance and Polymorphism
Note: Some functions in this case make also use of ‘embedded code sections’ in other programming languages
The following simple Dpdl example shows how the type class can make use of Inheritance and Polymorphism. Some functions in this example make use of embedded code sections implemented in ‘Java’ and ‘C’
Here is the link for the full Dpdl code of the example that is summarized below:
struct property {
int max_weight_gr
float max_height_m
string desc = null
}
class Animal {
int id
string name
struct property info = {100000, 2.5,.}
func Animal(int id_)
id = id_
name = "No name"
println("new Animal() with id: " + id + " info: " + info)
end
func Animal(int id_, string name_)
id = id_
name = name_
println("new Animal() with id: " + id + " and name: " + name + " - info: " + info)
end
func print()
println("This is an Animal")
end
func makeSound()
println("kind of animal is not defined")
end
func getHashMap()
object h_map = new("HashMap")
info_arr[] = array(info)
int i = 0
for(i < info_arr.size())
h_map.put(i, info_arr[i])
i=i+1
endfor
return h_map
end
}
class Dog : Animal {
func Dog(int id_, string name_)
super(id_, name_)
info.max_weight_gr = 8000
info.max_height_m = 0.5
info.desc = "this breed is Shitzu"
println("new Dog() with id: " + id + " and name: " + name + " - info: " + info)
end
func print()
println("This is a Dog with name: " + name)
end
func makeSound()
...
// check link above for complete implementation of this example
// now we can use the class
class Dog mydog(2, "Rosa")
mydog.print()
mydog.makeSound()
int sd = mydog.makeSound(10)
object map_dog = mydog.getHashMap()
println("map dog: " + map_dog)
var entry_di = map_dog.get(0)
println("1st entry: " + entry_di + " is of type: " + typeof(entry_di))
...
Compress and decompress data using the Java JRE Platform API
Dpdl example that uses java.util.GZIP* classes to compress and de-compress data
# main
object str = new("String", "my data to compress")
println("string to compress: " + str)
object byte_out = new("ByteArrayOutputStream")
object zip_out = new("GZIPOutputStream", byte_out)
println("compressing...")
zip_out.write(str.getBytes("UTF-8"))
zip_out.close()
println("data compressed successfully!")
object compressed_str = byte_out.toString()
println("compressed string: " + compressed_str)
println("decompressing...")
object byte_in = compressed_str.getBytes("UTF-8")
object byte_arr_in = new("ByteArrayInputStream", byte_in)
object byte_arr_in_obj = cast(byte_arr_in)
object zip_in = new("GZIPInputStream", byte_arr_in_obj)
object in_reader = new("InputStreamReader", zip_in)
object buf_reader = new("BufferedReader", in_reader)
string decompressed_str = ""
string line = ""
while(line != null)
line = buf_reader.readLine()
if(line != null)
decompressed_str = decompressed_str + line
fi
endwhile
println("decompressed: " + decompressed_str)
Bluetooth device discovery
Example Dpdl code that performs Bluetooth device discovery using high level Dpdl BT API :
int status = DPDLAPI_searchClientsOnServer()
int status_discovery = dpdlFalse
int service_discovery = dpdlFalse
int counter = 0
if(status == dpdlTrue)
while (status_discovery != dpdlTrue) && (service_discovery != dpdlTrue)
status_discovery = DPDLAPI_discoveryServerFinished()
service_discovery = DPDLAPI_serviceDiscoveryServerFinished()
print(".")
counter = counter+1
sleep(3000)
endwhile
string dev = "n"
int dev_found = 0
while(dev != "null")
dev = DPDLAPI_getServerVisibleBTAddr()
if(dev != "null")
println("bluetooth device visible: " + dev)
saveData(dev)
dev_found = dev_found + 1
fi
endwhile
else
println("No working Bluetooth stack found")
fi
Embedding of Python code
Python code can be embedded within Dpdl script by using the keyword ‘>>python’.
Example Dpdl script with embedded ‘Python’ code:
println("testing embedding python code wihin Dpdl")
println("")
>>python
languages = ['Dpdl', 'C', 'Python', 'OCaml']
for language in languages:
print(language)
<<
# again Dpdl
println("")
int exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
println("ebedded python exit code: " + exit_code);
Embedding C code
Dpdl allows the embedding and on-the-fly compilation and execution of C code directly within Dpdl scripts.
The C code can be embedded and executed with 2 distinct Modes, either interpreted only OR compiled and executed in memory at runtime.
The two modes have distinct properties: The interpreted C code execution is for example more convenient for testing, small footprint and portability, while the compiled C code execution is more convenient for faster execution and for linking with external libraries. The execution of C code is driven by a native Dpdl library that has a small footprint and for the interpreted mode it includes all essential C libraries and language constructs (ISO standard C90), POSIX compliant) with no external library dependencies needed. Custom libraries and functions can be integrated and linked via a straight forward implementation configuration approach.
Example Dpdl script with embedded C code (interpreted):
# main
# starting with Dpdl, pushing parameters on the stack and embedding C code
println("testing embedded C code in Dpdl")
int n = 6
double x = 10.0
string a = "test"
dpdl_stack_push(n, x, a)
>>c
#include <stdio.h>
int dpdl_main(int argc, char **argv){
printf("Hello C from Dpdl!\n");
printf("\n");
printf("num params: %d\n", argc);
int cnt;
for (cnt = 0; cnt < argc; cnt++){
printf(" param %d: %s\n", cnt, argv[cnt]);
}
return 0;
}
<<
# again Dpdl...
int exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
println("embedded C exit code: " + exit_code);
object str = new("String", "Dpdl embedded C")
bool b = str.contains("C")
println("Dpdl contains C: " + b)
This is a more complete example of the usage of embedded C code within Dpdl:
Embedding of ‘Julia’
Julia is a powerful and performant computational programming language (https://julialang.org)
Julia code can be embedded within Dpdl via the keyord ‘>>julia’
Example Dpdl script embedding ‘Julia’ that generates a Plot and saves it as PDF:
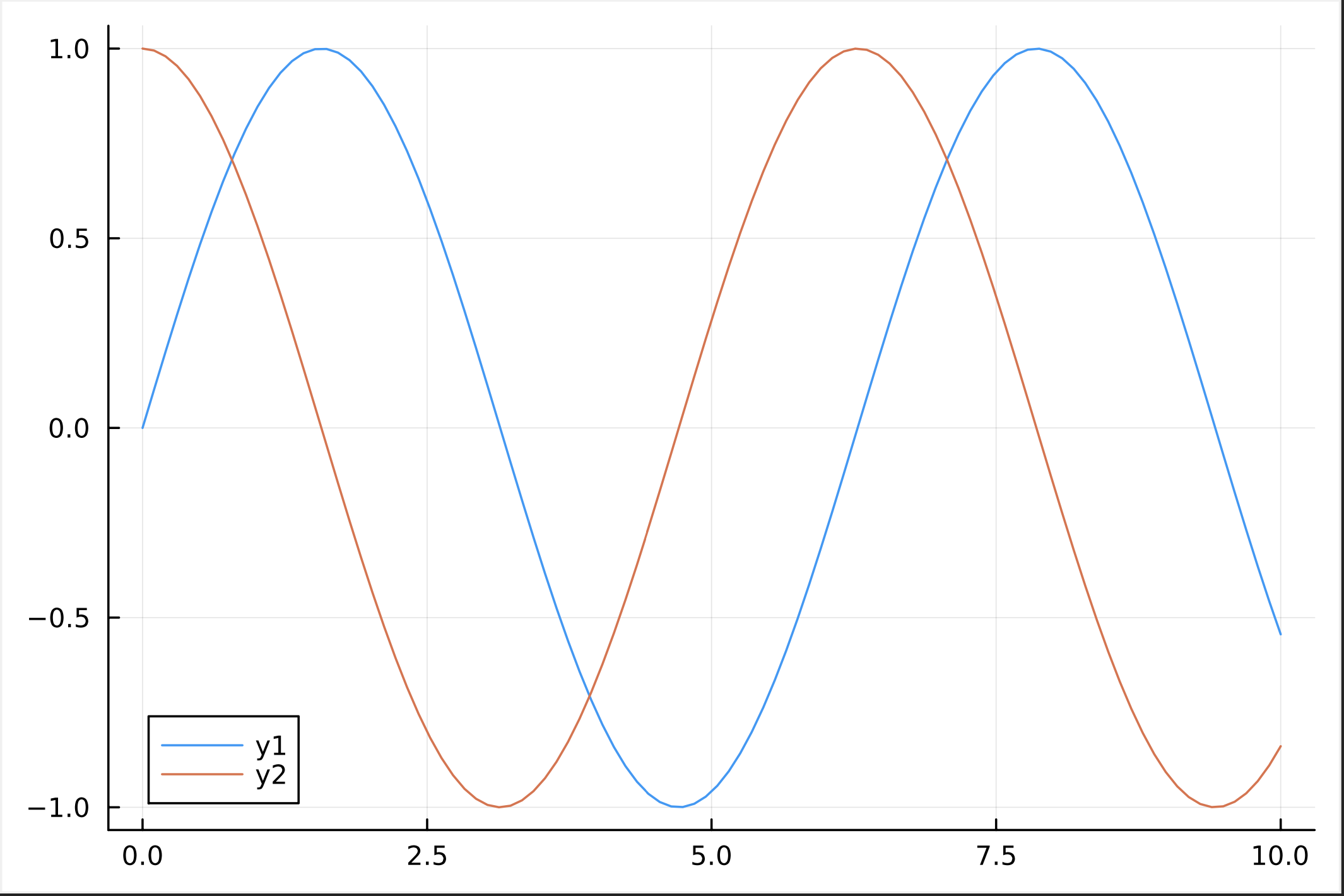
#main
println("Testing Plot data with Julia programming language...")
>>julia
using Plots
x = range(0, 10, length=100)
y1 = sin.(x)
y2 = cos.(x)
p = plot(x, [y1 y2])
savefig(p, "./Test/myplot.pdf")
dispose_status = @ccall dpdl_julia_dispose()::Int32
return 1
<<
int exit_code = dpdl_exit_code()
println("finished with exit code: " + exit_code)
Other programming languages
Other programming languages or natural language interpreters can be easily integrated in Dpdl via a dedicated plug-in interface and configuration in form of ‘Dpdl language plug-ins’. Please feel free to suggest yours favorite language on the Discussion section on the DpdlEngine GitHub repository
More Examples
Request free trial ‘DpdlEngine lite’
The ‘DpdlEngine lite’ release can be requested as Free trial shareware (with some limitation/restrictions) at the following request form:
The ‘DpdlEngine pro’ instead is available with custom licensing models only.
How to buy a ‘full’ DpdlEngine license?
To buy a full featured ‘DpdlEngine lite’ license with no limitations/restrictions, regular updates and support, please submit your request via the following request form:
For custom requirements or a bulk reseller license write an e-mail to the contact address.
Contact
e-mail: info@dpdl.io